Reduce your carbon footprint – and help the planet – with Sonac feed ingredients
Did you know the carbon footprint (CFP) of many of our products is a lot lower than that of vegetable alternatives? Partnering with Sonac does not just mean accessing quality feed ingredients, it also means boosting your sustainability performance – and helping the planet.
Working with Agri-footprint and Wageningen University & Research to cut CO2 emissions
A carbon footprint is the volume of greenhouse gases — primarily carbon dioxide, or CO2 — released into the atmosphere by an individual, organization or product. As CFPs have serious consequences for climate change and the environment, we all need to work together to bring CO2 emissions down. At Sonac we take this responsibility very seriously. We are constantly working with others to find ways of producing innovative ingredients from animal by-products with the lowest CFP possible. For example:
- Our CFP assessment methodology is in line with that used by Agri-footprint.com, a leading assessment specialist in agriculture. We share their aim to facilitate transparency and a more rapid transformation to sustainable food and feed supply chains.
- We also work with Wageningen University & Research (WUR), the publisher of a Carbon Footprint Animal Nutrition (CFPAN) tool and database called FeedPrint. The FeedPrint tool was developed to gain insight into greenhouse gas emissions during the production and utilization chain of feed and to identify mitigation options. Feed chain players can use it free of charge.
5 ways in which our solutions for feed will reduce your footprint
Our feed ingredient solutions contribute to smaller carbon footprints in several ways. Here are five:
- Using animal by-products in feed results in a smaller CFP than using the same by-products to create fuel or fertilizer
- The animal proteins in our feed ingredients have high digestibility levels, thereby improving feed efficiency and reducing CFP
- The proteins, minerals, fats, gelatins and numerous other specialty ingredients we create from animal by-products all have lower CFPs than those from alternative sources (more on this below)
- Our raw materials are locally sourced and locally sold, reducing CO2-intensive transportation mileage
- Our residuals-to-resources concept creates value from otherwise unused products, again decreasing CFP
Many of our ingredients outperform vegetable alternatives
Our feed ingredients are derived from animal by-products that would otherwise go unused. Many of these products have a lower carbon footprint than their vegetable alternatives.
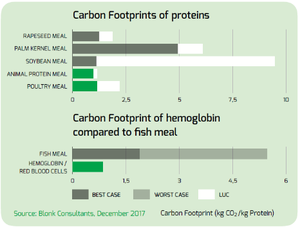
- The carbon footprint of our poultry meal products for the feed industry – measured per kilogram of protein – is more than 30% lower than that of rapeseed meal, according to independent research conducted by Blonk Consultancy in the Netherlands. Rapeseed meal is the best-performing vegetable meal, outperforming other vegetable products, such as soybean meal and palm kernel meal.
- The emissions related to land use and land use change (so-called LULUC) are also higher for vegetable meals than for animal by-product-based ingredients. In terms of Land-Use-Change (LUC), soybean and palm kernel meal have higher carbon footprints than animal proteins. The CFP of Hemoglobin is just one-third of that of fish meal (see graph).
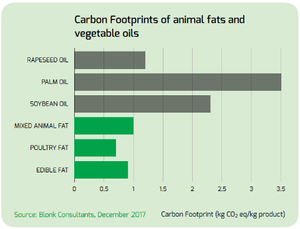
- The carbon footprints of our poultry fat, mixed fat and food grade fat products are much lower than the footprints of soybean oil, rapeseed oil and palm oil. Soybean and rapeseed oil reportedly emit nearly 2,000 kg CO2eq per ton, while palm kernel oil emits over 3,000 kg. Our food grade and poultry fats emit less than 1,000 and our mixed fat produces under 500 kg CO2eq per ton (see graph).
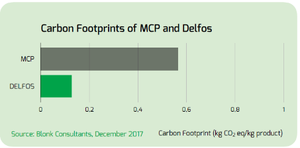
- Our organic phosphate for the feed industry, Delfos, leaves a carbon footprint that is 60% lower than that of inorganic mono-calcium phosphate (see graph).
- The LULUC emissions are also higher for vegetable oils than for our animal oils. The reason is that relatively large tracts of land are needed for the production of vegetable oils, which is causing large-scale deforestation in South America and Southeast Asia.
Reduce CO2 emissions, boost circular production
Sonac Feed relies on the use of edible and inedible organic residuals to create innovative and sustainable solutions. The more you tap into our solutions, the more you contribute to CO2 emission reduction and the creation of circular production systems.
Contact Sonac today for queries, quotes or further information.